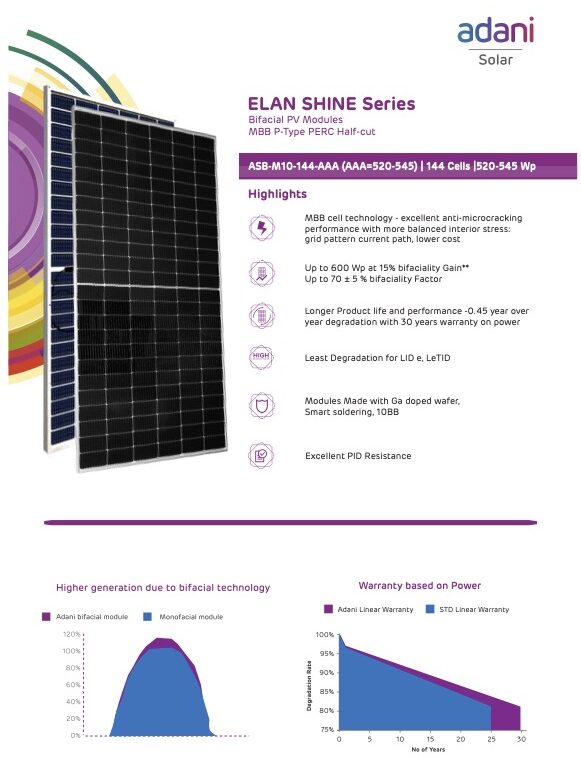
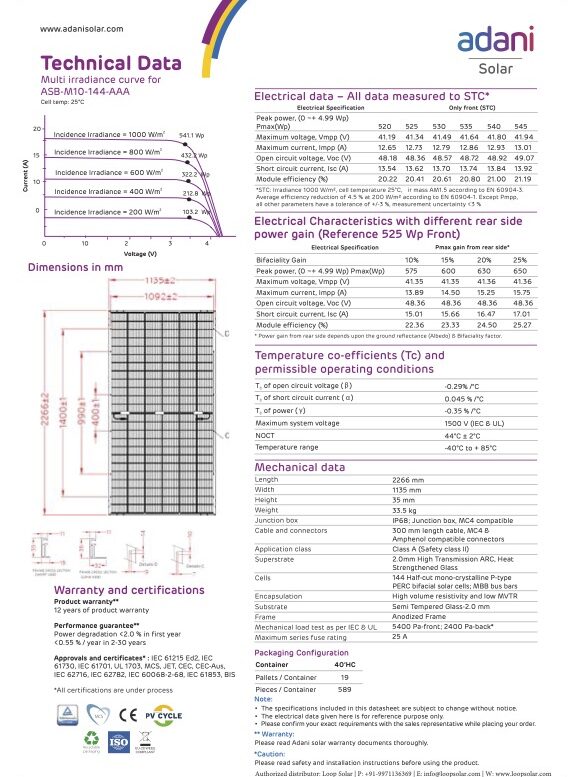
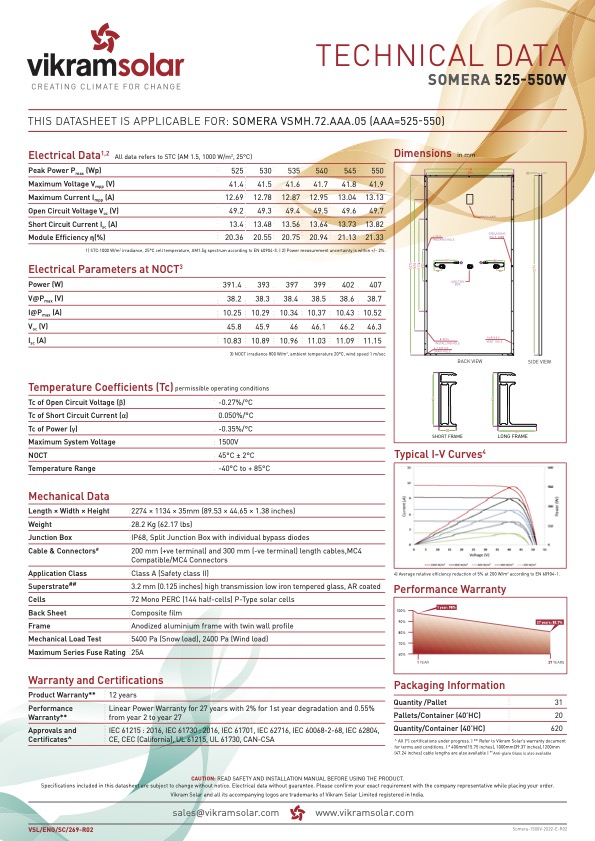
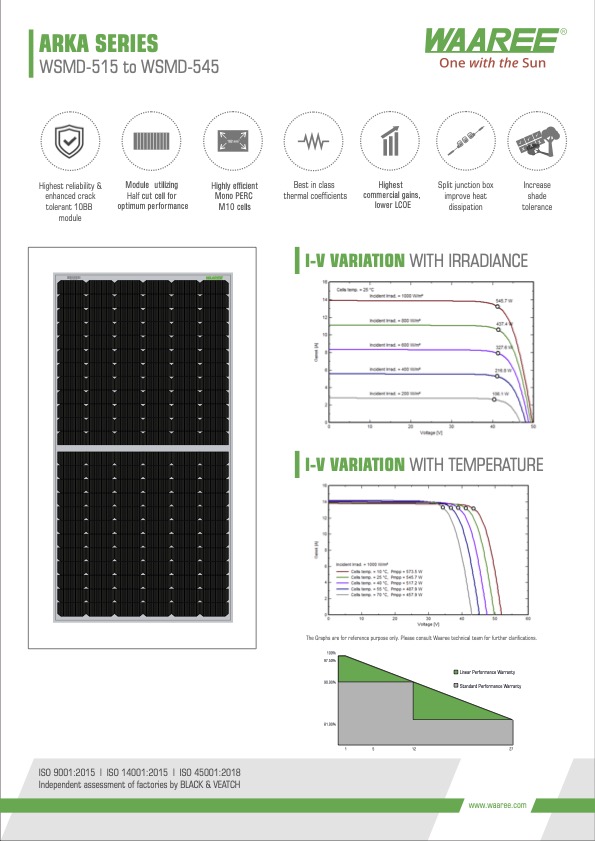
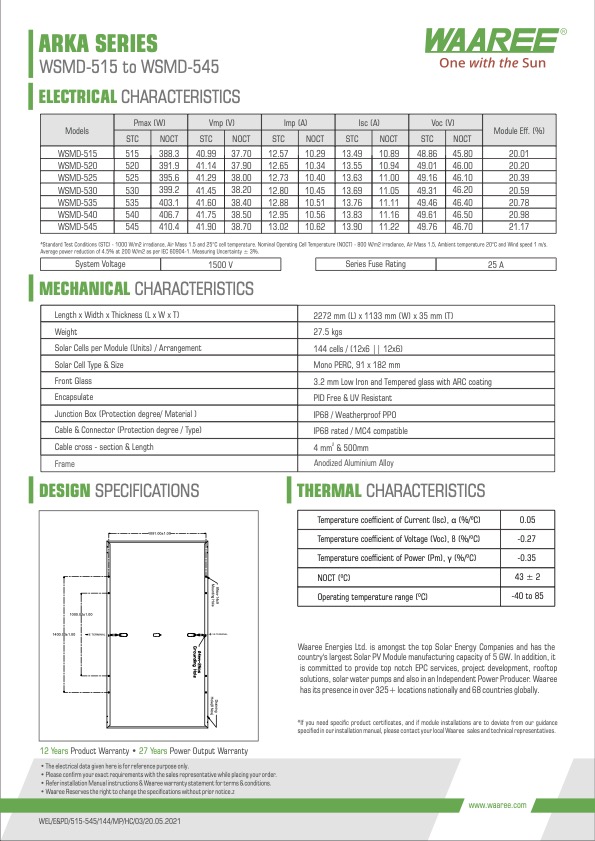
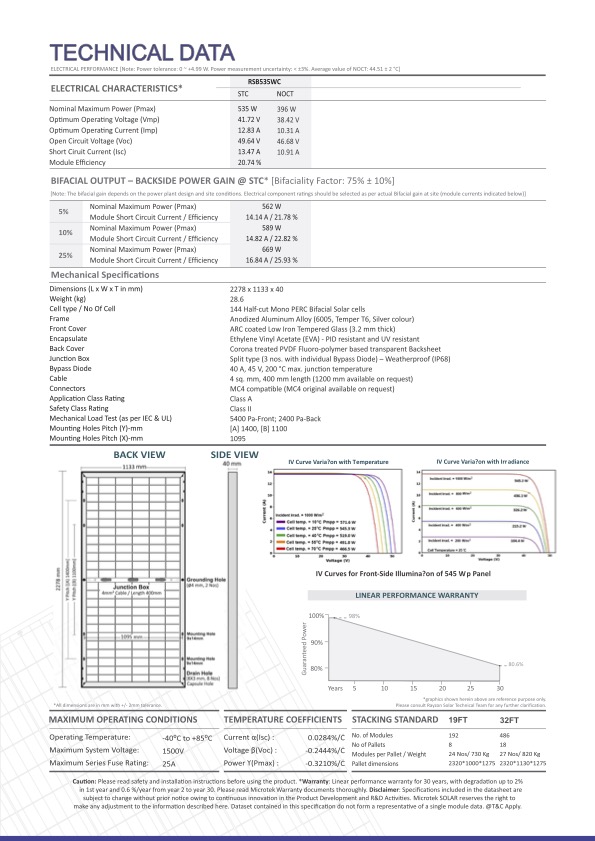
Our Products

On Grid System
Solar on-grid systems, also known as grid-tied or grid-connected systems, are a revolutionary way to generate clean energy for your home or business while remaining connected to the electrical grid for backup power. This detailed guide explores the functionalities, benefits, and considerations of installing a solar on-grid system on your property.
How Does a Solar On-Grid System Work?
The core components of a solar on-grid system include:
Solar Panels: These panels capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity through the photovoltaic effect.
Inverter: This crucial component transforms the DC electricity from the solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, compatible with the electrical grid and household appliances.
Net Meter (optional, depending on location): This meter tracks the electricity flow between your solar system and the grid. It measures the electricity you consume from the grid and the excess electricity you export back to the grid.
Grid Connection: Your system connects to the utility grid through a meter and safety devices, allowing you to import and export electricity as needed.
Applications of On Grid Solar System
- Domestic
- Individual Houses & Villas
- Residential High Raised Apartments
- Gated Communities
- Group Housing Societies
- Commercial Units
- Hospitals
- Hotels
- Resorts
- Restaurants
- Educational Institutions
- Research Centers
- Super Markets
- Banks
- Jewelry Shops
- Food Courts
- Cinema Theaters
- Industrial Units
- Manufacturing / Factory Units
- Food Processing Units
- Steel Industries

Benefits of a Solar On-Grid System:
Cost Savings: By offsetting your electricity usage with solar power generation, you can significantly reduce your electricity bills. The more solar energy you produce, the greater your cost savings.
Net Metering Benefits: Net metering programs allow you to earn credits for excess electricity exported to the grid. These credits can be used to offset electricity drawn from the grid during low-sunlight periods, maximizing your financial benefits.
Grid Stability: Solar on-grid systems contribute to a more stable and reliable electricity grid. By injecting clean, renewable energy during peak demand periods, they reduce strain on traditional power sources.
Environmental Impact: Solar energy is a clean and renewable resource. By choosing a solar on-grid system, you significantly reduce your carbon footprint and contribute to a cleaner, healthier planet.
Increased Property Value: Studies have shown that homes with solar panels tend to sell faster and for a higher price compared to similar homes without solar.
* MNRE Subsidy Available

Off Grid System
Unlike its grid-tied counterpart, a solar off-grid system operates independently of the utility grid. Here are the key components involved:
Solar Panels: Similar to on-grid systems, solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into DC electricity.
Solar Charge Controller: This vital component regulates the flow of electricity from the solar panels to the batteries, preventing overcharging and extending battery life.
Batteries: The heart of an off-grid system, batteries store excess solar energy generated during the day for use at night or during low-sunlight periods.
Inverter: As with on-grid systems, the inverter converts the stored DC electricity from the batteries into AC electricity usable by your appliances and lights.
system’s functionality:
1. Solar Energy Capture: Sunlight strikes the solar panels, generating DC electricity.
2. Power Regulation: The solar charge controller regulates the DC electricity flow from the panels to the batteries.
3. Battery Storage: Excess electricity produced during peak sunlight hours is stored in the batteries for later use.
4. Power Conversion: When needed, the inverter converts the stored DC electricity from the batteries into AC electricity.
5. Powering Your Needs: The converted AC electricity powers your appliances and lights.

Benefits of a Solar Off-Grid System:
Energy Independence: The primary advantage of a solar off-grid system is complete freedom from the utility grid. You generate your own clean energy and are not reliant on fluctuating electricity prices.
Remote Location Compatibility: Off-grid systems are ideal for locations far from the reach of the electrical grid, allowing you to enjoy the benefits of solar power anywhere.
Disaster Preparedness: With a properly sized battery bank, you can ensure a consistent power supply during outages or natural disasters.
Environmental Sustainability: Solar energy is a clean and renewable resource. Choosing an off-grid system minimizes your dependence on fossil fuels and reduces your carbon footprint.
Potential Cost Savings: Over time, the reduction in electricity bills can outweigh the upfront investment costs of the solar system, especially in areas with high electricity rates.
Applications of Off Grid Solar Power Plant
- Domestic
- Individual Houses & Villas
- Commercial Units
- Hospitals
- Hotels
- Resorts
- Restaurants
- Educational Institutions
- Research Centers
- Super Markets
- Banks
- Jewelry Shops
- Food Courts
- Industrial Units
- Manufacturing / Factory Units
- Food Processing Units

EV Charging
Imagine fueling your electric vehicle (EV) with clean, home-grown energy – that’s the beauty of solar EV charging! This innovative solution combines the power of the sun with the efficiency of electric vehicles, creating a sustainable and cost-effective way to keep your car moving. This detailed guide explores the functionalities, benefits, and considerations of integrating solar power with your EV charging at home.
How Does Solar EV Charging Work?
A solar EV charging system typically consists of three key components:
Solar Panels: These panels capture sunlight and convert it into DC electricity.
Solar Inverter: This device transforms the DC electricity from the panels into AC electricity compatible with your EV charger.
EV Charger: A dedicated EV charger, installed at your home, safely and efficiently delivers AC electricity to your EV’s battery.
Here’s a breakdown of the charging process:
1.Sun’s Energy Captured: Sunlight strikes the solar panels, generating DC electricity.
2. Power Conversion: The solar inverter converts the DC electricity into AC electricity.
3. Charging Your EV: The converted AC electricity flows from the inverter to the EV charger, which then safely charges your electric vehicle’s battery.
Integration with the Grid (Optional):
Grid-Tied System: You can connect your solar system to the electrical grid. During peak sunshine hours, excess solar energy can be exported to the grid, potentially earning you credits. When solar production is insufficient, you can draw power from the grid to supplement your EV charging needs.

Benefits of Solar EV Charging:
Cost Savings: By offsetting your EV charging needs with solar energy, you can significantly reduce your reliance on the grid and potentially lower your electricity bills.
Environmental Sustainability: Solar power is a clean and renewable resource. Charging your EV with solar energy reduces your carbon footprint and promotes a cleaner future.
Increased Home Value: Homes with solar panels and EV charging capabilities are becoming increasingly desirable, potentially leading to a higher property value.
Energy Independence (Off-Grid Systems): For those seeking complete energy independence, off-grid solar EV charging offers the ultimate solution, minimizing reliance on the traditional electricity grid.
Off-Grid System (For Advanced Users): A more complex setup involves an off-grid solar system with a larger battery bank. This allows you to store excess solar energy for EV charging even during low-sunlight periods, achieving a higher degree of energy independence.
Applications of Off EV Charging
- Domestic
- Individual Houses & Villas
- Residential High Raised Apartments
- Gated Communities
- Group Housing Societies
- Commercial Units
- Hospitals
- Hotels
- Resorts
- Restaurants
- Super Markets
- Food Courts
- Cinema Theaters

Heat Pump
Solar heat pumps offer a revolutionary approach to heating your home or business, utilizing the sun’s energy for an efficient and eco-friendly solution. This detailed guide explores the functionalities, benefits, and considerations of integrating solar technology with heat pumps to create a comfortable and sustainable heating system.
Understanding Solar Heat Pumps:
A solar heat pump system combines two powerful technologies:
Solar Thermal Collectors: These panels, similar to rooftop solar panels, capture the sun’s heat energy.
Air-Source Heat Pump: This versatile appliance extracts heat from the surrounding air (even in cold weather) and amplifies it to warm your space.
There are two main types of solar heat pump systems:
Solar-Assisted Air-Source Heat Pump: In this system, the solar thermal collectors preheat a water glycol mixture. This preheated liquid is then used by the heat pump to extract even more heat from the air, resulting in a more efficient heating process.
Direct Expansion Solar Heat Pump: This system uses a refrigerant instead of a water glycol mixture. The solar thermal collectors directly heat the refrigerant, which then enters the heat pump for further temperature increase, maximizing solar energy utilization.
How Does a Solar Heat Pump System Work?
1. Sun’s Energy Captured: Sunlight strikes the solar thermal collectors, heating the transfer fluid (water glycol mixture or refrigerant).
2. Heat Transfer: The heated fluid is circulated to the heat pump.
3. Heat Pump Amplification: The heat pump extracts additional heat from the preheated fluid and the surrounding air, significantly boosting the overall heating output.

Benefits of Solar Heat Pumps:
Increased Efficiency: Solar heat pumps significantly reduce the reliance on traditional electric or gas heating systems, leading to lower energy bills.
Sustainable Heating: By harnessing solar energy, a renewable resource, solar heat pumps minimize your carbon footprint and contribute to a cleaner environment.
Government Incentives: Many regions offer financial incentives to encourage the adoption of solar heat pumps, reducing the upfront investment costs.
Reduced Reliance on Fossil Fuels: Solar heat pumps lessen your dependence on traditional heating sources, potentially offering greater energy independence.
Year-Round Comfort: While primarily used for heating, some solar heat pumps can also be used for air conditioning in the summer months, providing year-round comfort control.
4. Space Heating: The amplified heat is distributed throughout your home or business using existing ductwork (if available) or radiant floor heating systems.
Applications of Heat Pump Water Heaters
- Domestic
- Individual Houses & Villas
- Residential High Raised Apartments
- Commercial Units
- Hospitals
- Hotels & Lodges
- Resorts
- Textile & Garment Industry
- Research Centers
- Industrial Units
- Food Processing Units
- Dairy Processing Units